Cosmic-Ray Muon
The detectors are susceptible to noise signals. Occasionally muons produced by the cosmic-ray pass through the detector and produce unwanted signals, decreasing the accuracy and precision of the experiment.
Shielding Antineutrino Detectors From Background
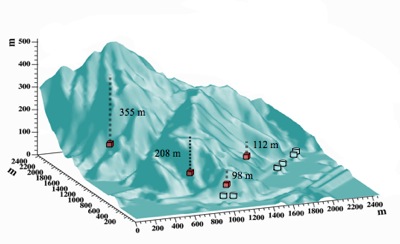
Mountain Profile
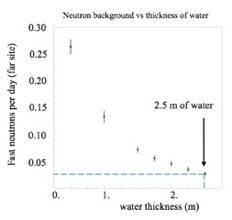
Each antineutrino detector is enclosed by 2.5 m of water to shield energetic neutrons produced by cosmic-ray muons and gamma-rays from the surrounding rock.
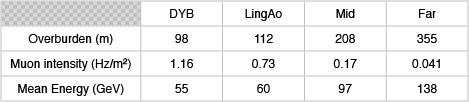
In order to study the background generated by cosmic-ray muons, a modified Gaisser parametrization is used for the cosmic-ray flux at the surface. Then a software code called MUSIC is used to estimate the muon intensity and energy at the underground halls based on the mountain profile.
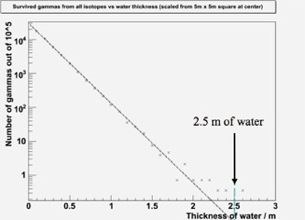
Surviving gamma rays vs. thickness of water.
Neutron background vs. thickness of water.
Background
Below is an example of muon system:
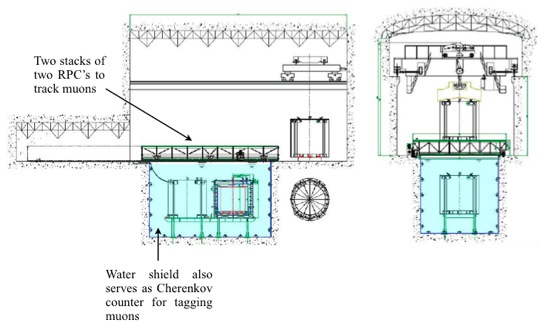
Uncorrelated Background:
Sources: U, Th, K, Rn, neutron
1. Single gamma rate @ 0.9MeV < 50Hz/antineutrino detector
2. Single neutron rate < 1000/day/antineutrino detector
Correlated Background:
1. Fast Neutrons: double coincidence
2. 8He/9Li: beta-neutron emitting decays
University of California, Berkeley | LBL 50A-2112 | Administrator: Shuo Wang
So, what is θ13?



